Wondering how fat exits your body during weight loss or after a CoolSculpting treatment? Let’s explore the common questions often raised by clients at Element Body Lab. While we specialize in CoolSculpting, misconceptions about weight loss versus our treatments are very common. CoolSculpting is a nonsurgical treatment that targets unwanted fat in specific areas of the body, not intended for overall weight loss. Typically, clients seeking CoolSculpting are already at or near their ideal weight and are looking to address localized areas of stubborn fat. But it can be confusing, demystifying weight loss and understanding weight loss vs. CoolSculpting. Learn more about how CoolSculpting works for fat reduction.
Many myths surround targeted weight loss, a common concern for clients seeking solutions to fat pockets resistant to diet and exercise. Despite efforts to target specific areas with exercise, weight loss tends to occur uniformly across the body rather than in isolated regions.
Lastly, let’s delve into fat metabolism and excretion: everything from understanding how the body burns fat to the process of eliminating fat cells. Fat metabolism involves complex biochemical processes that break down stored fat into energy, while the elimination of fat cells occurs through various bodily mechanisms. Understanding these processes can provide valuable insights into achieving effective weight loss and body contouring goals.
How weight loss works
Weight loss works through a complicated mix of physiological processes that work to reduce body fat. Simply put, people lose weight when there is a deficit of calories. The equation is simple:
More calories out than in leads to weight loss.
When you consume fewer calories than your body needs to use for energy purposes, it taps into its fat stores, leading to weight loss. The process involves the breakdown of triglycerides, the storage form of fat, into fatty acids and glycerol, which are released into the bloodstream. These components are then utilized by cells for energy production.
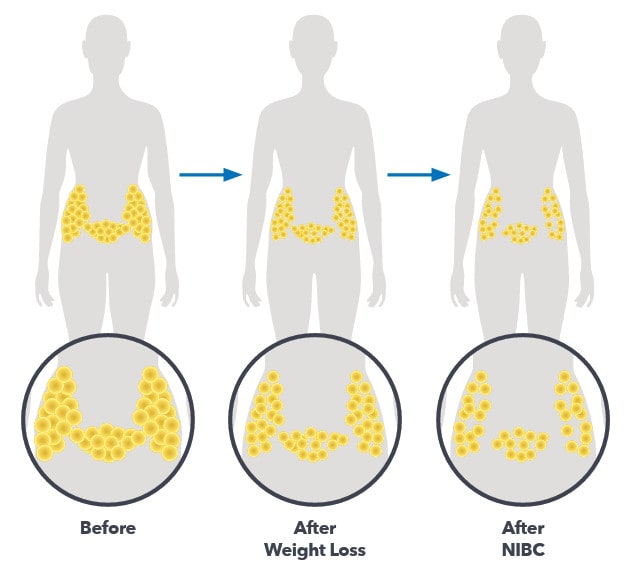
Alternatively, when you pursue surgical options like liposuction or a non-invasive body contouring (NIBC) treatment, you’re permanently killing and removing fat cells.
Weight Loss Vocabulary Terms:
- Triglyceride: A stored triglyceride is a type of fat molecule that your body stores in fat cells for energy. It consists of three fatty acid molecules bonded to a glycerol molecule. When you consume more calories than your body needs, the excess energy is converted into triglycerides and stored in fat cells throughout your body, ready to be used as fuel when needed.
- Fatty Acid: A fatty acid is a type of molecule that serves as a building block of fat. It is composed of a long chain of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms, with a carboxylic acid group at one end. Fatty acids are crucial for various biological processes in the body, including energy production, cell membrane structure, and hormone regulation. They can be saturated (with all single bonds between carbon atoms) or unsaturated (containing one or more double bonds between carbon atoms), and their structure determines their function and impact on health.
- Glycerol: Glycerol, also known as glycerin, is a simple polyol compound that serves as a building block for fats and oils. It is a colorless, odorless, and sweet-tasting substance that is commonly used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Glycerol plays a crucial role in the body as part of triglycerides, which are the primary constituents of fat molecules stored in adipose tissue. During metabolism, triglycerides are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids, which can then be utilized for energy production or stored for future use. Glycerol also acts as a humectant, helping to retain moisture in the skin and prevent dehydration.
Translation? When you eat less food than your body needs for energy, it uses up stored fat to make up the difference. Fat gets broken down into tiny parts called fatty acids and glycerol, which your body uses to make the energy it needs to survive.
Additionally, hormonal changes, such as increased levels of adrenaline and noradrenaline stimulate the breakdown of fat cells, which also facilitates fat loss. Regular exercise further enhances this process by increasing metabolism and promoting fat oxidation. Over time, these mechanisms contribute to a decrease in overall body fat and promote weight loss.
What is fat oxidation?
Fat oxidation, also known as lipid oxidation or fat metabolism, is the process by which fatty acids are broken down and converted into energy within the body. It involves the biochemical pathways that allow cells to extract energy from stored fat molecules for use in various physiological functions.
During fat oxidation, stored triglycerides in adipose tissue are hydrolyzed into glycerol and fatty acids. These fatty acids are then transported to the mitochondria, the cell’s powerhouse, where they undergo a series of chemical reactions known as beta-oxidation. In beta-oxidation, fatty acids are sequentially broken down into acetyl-CoA molecules, which enter the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The ATP generated through fat oxidation can be used to fuel cellular activities, including muscle contraction, metabolism, and other physiological processes.
Fat oxidation is a crucial component of energy metabolism, especially during periods of low glucose availability, such as fasting or prolonged exercise. It helps maintain energy homeostasis by providing an alternative fuel source when carbohydrates are scarce or depleted. Increasing fat oxidation through exercise and dietary interventions is often a goal for individuals aiming to lose weight or improve metabolic health.
Translation? When you exercise or feel excited, your body releases special hormones that help break down fat cells. This makes it easier for your body to use fat for energy, especially when you exercise regularly. As time goes on, these actions help reduce the amount of fat in your body and lead to weight loss.
How Hormones Impact Fat Metabolism
Let’s cover some of the hormones that impact fat metabolism:
- Insulin: Regulates blood sugar levels and promotes fat storage when levels are high.
- Glucagon: Acts in opposition to insulin, stimulating the breakdown of stored glycogen and fat for energy.
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine): Triggers the release of fatty acids from fat stores during periods of stress or physical activity.
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine): Similar to adrenaline, it promotes the breakdown of fat for energy production.
- Leptin: Regulates appetite and metabolism by signaling satiety to the brain and increasing energy expenditure.
- Ghrelin: Stimulates appetite and promotes fat storage when levels are elevated.
- Cortisol: Released in response to stress, it can promote the breakdown of muscle tissue for energy and lead to increased fat storage, particularly in the abdominal region.
Understanding the intricate interplay of hormones is essential for grasping how fat metabolism is regulated within the body. Hormones such as insulin, glucagon, adrenaline, noradrenaline, leptin, ghrelin, and cortisol play pivotal roles in orchestrating processes like appetite control, energy expenditure, and the utilization of fat stores for energy production.
Insulin, for instance, manages blood sugar levels and facilitates fat storage when levels are elevated. Conversely, glucagon acts as its counterpart, stimulating the breakdown of stored glycogen and fat to provide energy during times of low blood sugar.
During periods of stress or physical exertion, adrenaline and noradrenaline kick into action, triggering the release of fatty acids from fat stores to meet the body’s increased energy demands. Meanwhile, leptin communicates feelings of satiety to the brain, curbing appetite and boosting metabolism, while ghrelin stimulates hunger and encourages fat storage when levels are heightened.
Cortisol, released in response to stress, can have dual effects on fat metabolism. While it promotes the breakdown of muscle tissue for energy, it can also lead to increased fat storage, particularly in the abdominal region.
These hormones function synergistically to maintain energy balance and regulate fat metabolism in response to various internal and external stimuli. For instance, insulin promotes fat storage, while adrenaline facilitates the release of fatty acids during periods of physical activity.
Moreover, many of these hormones exhibit reciprocal relationships. For example, insulin and glucagon work in tandem to regulate blood sugar levels: insulin promotes glucose uptake and fat storage, while glucagon stimulates glycogen breakdown and fat mobilization when blood sugar levels are low.
Understanding the intricacies of hormone function empowers individuals to make informed choices regarding their diet, exercise regimen, and lifestyle habits to support effective fat loss and weight management. Furthermore, recognizing the role of hormones is particularly crucial when considering treatments like CoolSculpting for targeted weight loss, as hormonal balance can significantly influence fat distribution and elimination within the body.
When does your fat loosen when losing weight?
Fat loosens gradually as you lose weight, typically beginning after your body enters a calorie deficit and starts burning stored fat for energy.
As you continue to lose weight through a combination of diet and exercise, fat cells gradually release stored triglycerides, leading to a reduction in their size. This process continues over time as you maintain a consistent calorie deficit, resulting in further fat loss and eventual slimming of areas where fat was stored.
What are physical signs your body is burning fat?
Understanding how your body burns fat is crucial. Signs like increased energy and reduced waistline are long-term indicators of fat burning. You can look for some of the physical cues that your body is burning fat in the day-to-day and as you change your lifestyle habits:
- Increased Energy: Burning fat releases energy, making you feel more energetic during workouts or throughout the day.
- Sweating: Fat burning increases metabolism, leading to increased body temperature and sweating during exercise.
- Feeling Warm: Fat burning generates heat, causing your body to feel warmer, especially during physical activity.
- Increased Heart Rate: As your body burns fat for fuel, your heart rate may elevate to supply oxygen to working muscles.
- Improved Endurance: Over time, as your body becomes more efficient at burning fat, you may notice improved endurance during exercise sessions.
How to trigger fat burning process/ What triggers fat burn?
Contrary to many myths, there’s few ways to trick your body into triggering a fat burning process. To trigger the fat burning process, focus on a combination of diet and exercise. Incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT), strength training, and cardio workouts into your exercise routine. Needing some inspiration on workouts to trigger fat burn?
5 HIIT workouts to trigger fat burn:
- Tabata: Consists of 20 seconds of intense exercise followed by 10 seconds of rest, repeated for several rounds.
- Sprint Intervals: Alternating between short bursts of maximum effort sprinting and active recovery periods.
- Jumping Jacks: Perform as many jumping jacks as possible in a set time interval, followed by a brief rest.
- Burpees: Combine a squat, push-up, and jump into a single explosive movement, repeating for a set duration.
- Mountain Climbers: Quickly alternate bringing your knees towards your chest in a plank position, maintaining a fast pace for a set time.
HIIT workouts are particularly effective as they elevate your heart rate and boost metabolism, promoting fat burn even after you’ve finished exercising. Can’t bring yourself to do these? How about strength training instead?
5 Strength Training Exercises to trigger fat burn:
- Squats: Perform bodyweight squats or add resistance with weights to engage large muscle groups like the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Deadlifts: Lift a weighted barbell or dumbbells from the floor to hip level, engaging the posterior chain muscles including the lower back, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Lunges: Step forward or backward with one leg, lowering your body until both knees are bent at a 90-degree angle, then return to the starting position.
- Push-ups: Engage the chest, shoulders, and triceps by lowering and raising your body using your arms while maintaining a plank position.
- Pull-ups or Rows: Use a pull-up bar or resistance bands to perform exercises that target the muscles of the back, biceps, and shoulders.
Additionally, prioritize whole foods in your diet, including lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, vegetables, and complex carbohydrates.
Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat snacks, as they can hinder fat loss. Staying hydrated and getting enough sleep are also essential for optimizing fat metabolism and promoting overall health.
Methods to Burn Body Fat. How to burn body fat
The only way to effectively burn body fat is to trigger the fat burning process. Incorporate regular exercise and a balanced diet into your routine. Lifestyle changes, like stress management and quality sleep, support fat loss. Personalized plans with a certified trainer or dietitian can enhance results and help hold you accountable. The hardest part about effective weight loss options is sticking with the patterns and routines that work. It takes a lot of commitment, and a massive change in routine.
Clients looking to burn body fat quickly may choose to introduce medical weight loss options, such as semaglutide in order to help them more efficiently burn body fat.
How does fat leave your body when you lose weight? Do you actually lose fat cells during weight loss?
When you lose weight, fat cells become smaller as they release stored energy and waste. However, the number of fat cells usually stays the same.
These smaller, shrunken fat cells let out triglycerides, a kind of fat in your blood, which break down into fatty acis and glycerol. Your body uses these two things for energy.
As fat is burned, waste is removed through your lymphatic system, a network in your body that helps get rid of waste and toxins.
Does fat release toxins when you lose weight?
While fat cells shrink, they may also release metabolic waste products and certain toxins that were stored within the fat tissue. These toxins are not directly released into the bloodstream but are instead eliminated through various pathways as part of the body’s natural detoxification process.
One major route for toxin elimination is through urine, where water-soluble waste products are filtered by the kidneys and excreted from the body. Sweating also facilitates the removal of toxins through the skin, as sweat glands help expel water, electrolytes, and small molecules from the body. Additionally, breathing plays a role in toxin elimination, as volatile organic compounds and other waste products may be exhaled from the lungs.
While the reduction in fat cell size during weight loss contributes to overall detoxification, it’s essential to support the body’s natural detoxification pathways by staying hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and nutrients, and engaging in regular physical activity. These lifestyle habits can optimize the body’s ability to eliminate toxins and support overall health and well-being.
How to get rid of fat cells permanently: Surgical options and Non surgical options
Surgical procedures like liposuction remove fat cells permanently. Non-surgical alternatives like CoolSculpting freeze fat cells, causing them to crystallize and be naturally eliminated by the body. Both liposuction and CoolSculpting permanently remove fat cells. Learn more about how CoolSculpting works for fat reduction.
CoolSculpting – how it works
CoolSculpting, offered at Element Body Lab, is a non-invasive procedure that targets and eliminates stubborn fat cells. Our CoolSculpting Elite technology delivers precise cooling to targeted areas, resulting in gradual and natural fat reduction. Learn more about how CoolSculpting works for fat reduction.

Aftermath of CoolSculpting Treatment: Where does the fat go after a CoolSculpting treatment?
Following CoolSculpting, clients may experience temporary redness, swelling, or numbness in the treated area. Long-term effects include natural-looking fat reduction without surgery or downtime. Results are long-lasting with a healthy lifestyle.
The fat after a CoolSculpting treatment is eliminated through your lymphatic system. Simply put, your body naturally eliminates and excretes the dead fat in the same way that it eliminates toxins from the body during weight loss.
A more detailed explanation involves a deeper understanding of the lymphatic system itself. The lymphatic system is a vital part of the body’s immune system, consisting of a network of vessels, tissues, and organs that help remove toxins, waste, and other unwanted materials from the body. It works alongside the circulatory system to transport lymph, a fluid containing white blood cells and lymphocytes, throughout the body. The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in filtering and draining lymph fluid, fighting infections, and maintaining fluid balance within tissues. Additionally, lymph nodes, which are small bean-shaped structures located throughout the body, act as filters that trap and destroy harmful substances, such as bacteria and viruses, helping to protect the body from infection and disease. Learn more about how CoolSculpting works for fat reduction.
What are physical signs of fat leaving the body after CoolSculpting?
After a CoolSculpting treatment, there are few reports of physical signs that fat is leaving the body as it’s a gradual, natural process. Occasionally, clients at Element Body Lab report a difference in sweat, urine or stool.
For some, they notice the odor of sweat or urine is more notiecable. For others, they notice loose stool or diarrhea for a day or two. It’s nothing that would cause worry, but instead, might make you wonder what you ate in the last day or two.
Clinical studies have been conducted on CoolSculpting to evaluate the impact on major bodily functions, including liver function and lipid levels. These studies show that CoolSculpting is a safe and effective treatment option for clients without underlying health conditions. Of course, you’ll want to consult with a qualified medical professional and discuss your medical history prior to making a decision to pursue this treatment.
Are fat cells gone permanently after CoolSculpting?
Yes! CoolSculpting is a permanent solution for targeted fat loss. Once the fat is gone, it’s gone for good. Clients often pursue 2-4 sessions to any treatment area to achieve the full desired outcome, then maintain their results permanently with healthy diet and exercise choices.
You’ll want to protect your investment in CoolSculpting by maintaining your weight. While CoolSculpting is not a weight loss treatment, clients who are looking to lose weight often combine CoolSculpting to spot treat trouble areas either at the beginning of their weight loss journey, or to fine tune their results after weight loss. Learn more about how CoolSculpting works for fat reduction.
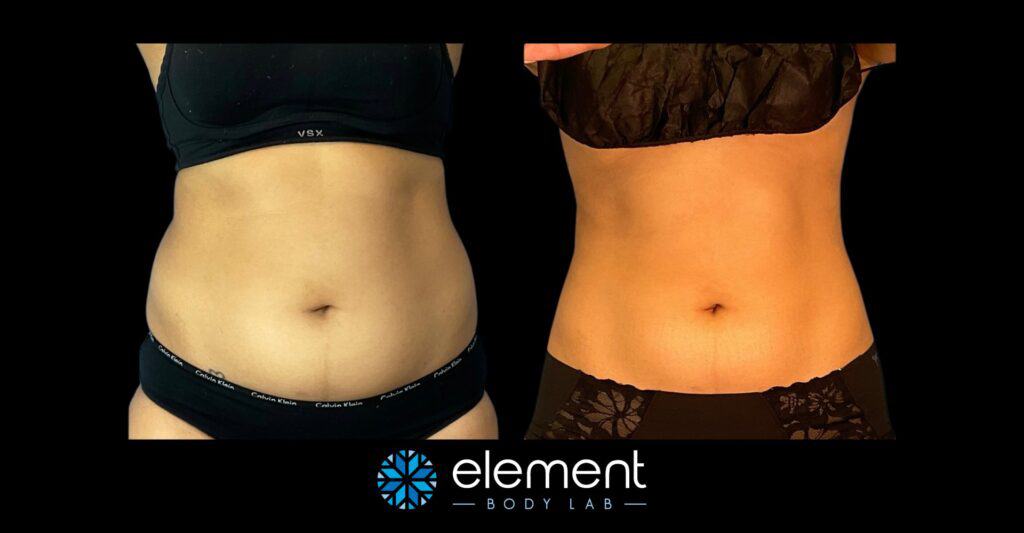
When learning about CoolSculpting, it can be hard to believe that you can see results like this, but not have any change in weight. That said, each of the clients depicted below had a nominal (less than 3 lb) change in weight, or no change at all.

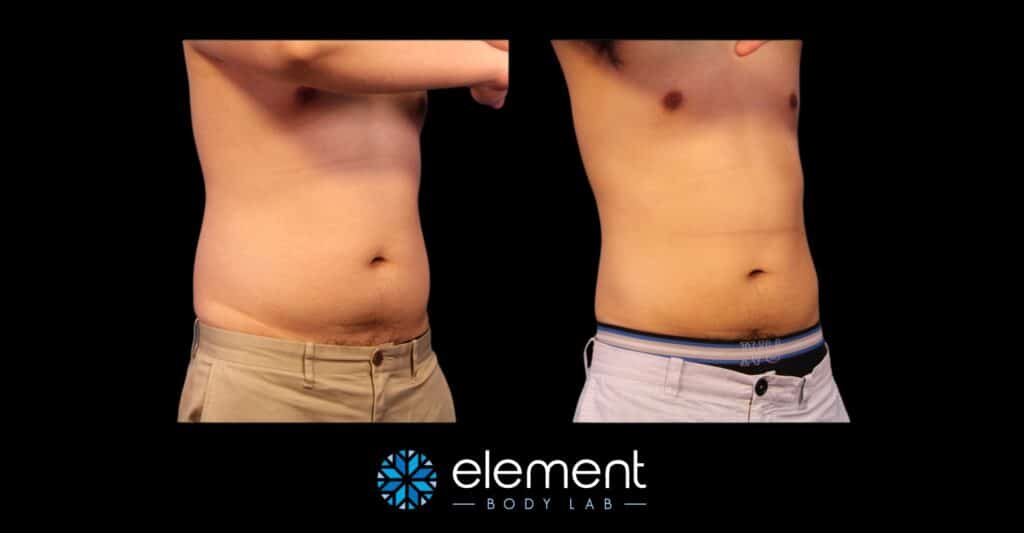
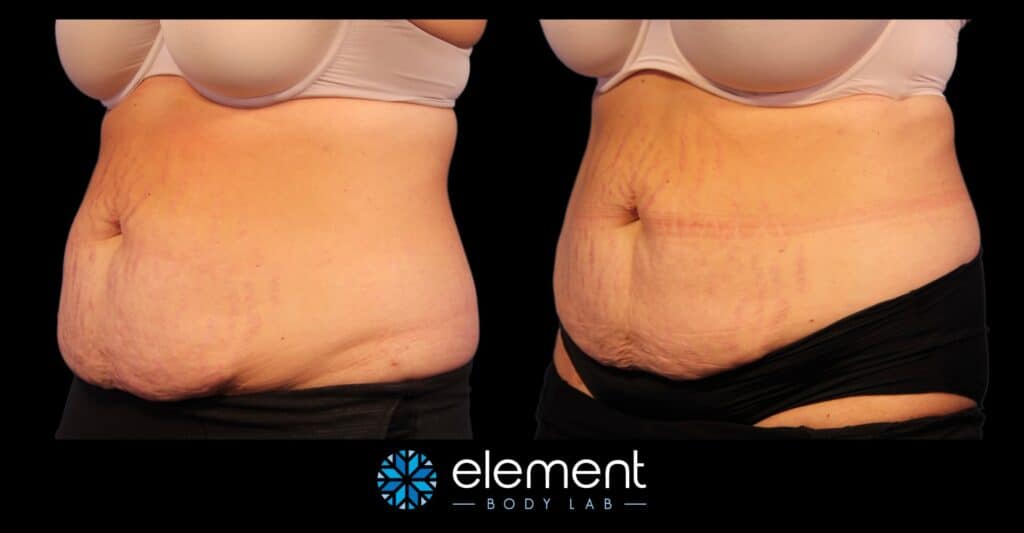
CoolSculpting Recovery and Potential Side Effects
After a CoolSculpting treatment, clients may experience temporary side effects such as redness, swelling, or numbness in the treated area. These effects usually subside within a few days to weeks. Some clients may also experience sensations of tingling, stinging, or discomfort during or after the procedure, which typically resolve on their own. It’s essential to follow post-treatment care instructions provided by your provider to ensure optimal results and minimize any discomfort.
While rare, more severe side effects like paradoxical adipose hyperplasia (an increase in fat volume in the treated area) or changes in sensation may occur. However, these are uncommon and will be discussed during a consultation with our team. Overall, CoolSculpting is a safe and effective procedure with minimal downtime, allowing clients to return to their normal activities immediately after treatment. Learn more about how CoolSculpting works for fat reduction.
Learn more about CoolSculpting Elite with Element Body Lab
Understanding fat metabolism and excretion is key to achieving your body goals. At Element Body Lab, we’re committed to providing personalized solutions for our clients. Schedule a consultation with us to explore non-surgical fat reduction options tailored to your needs. Let’s embark on your journey to a slimmer, more sculpted physique together. Learn more about how CoolSculpting works for fat reduction.

